小白坚持刷 212 ~ 搜单词 2
基本信息
- 题号:212
- 题厂:脸书
- 难度系数:高
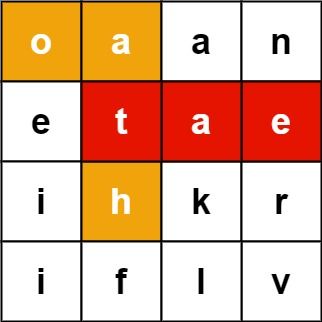
#79 升级版。
还是在 m * n 的矩阵中找单词。较 #79 不同的是,本次要搜寻一系列单词,如果单词出现在了矩阵中,则将出现单词以数组形式返回。
欲解 212,需先理解 79.
解题思路
- 按照 #79 的思路,可以先将目标单词根据单词首字母整理成 hashmap。再遍历矩阵,当格子和 hashmap 的 key 匹配时,再进行和 #79 类似的 上、下、左、右 四个方向查找。如果找到,则将单词添加进返回数组……
# 在 79 原理之上,引入 hashmap 的升级解法如下:
class Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
# 「首字母」:「首字母对应单词数组。。。」
wordList = {}
for word in words:
if word[0] not in wordList:
wordList[word[0]] = [word]
else:
wordList[word[0]].append(word)
row, col = len(board), len(board[0])
res = []
def findWord(word, r, c, i, path):
if i == len(word):
return True
if (r < 0
or r >= row
or c < 0
or c >= col
or (r, c) in path
or board[r][c] != word[i]):
return False
path.add((r, c))
res = (findWord(word, r + 1, c, i + 1, path)
or findWord(word, r - 1, c, i + 1, path)
or findWord(word, r, c + 1, i + 1, path)
or findWord(word, r, c - 1, i + 1, path))
path.remove((r, c))
return res
for r in range(row):
for c in range(col):
if board[r][c] in wordList:
for word in wordList[board[r][c]]:
if findWord(word, r, c, 0, set()) and word not in res:
res.append(word)
return res
- 以上解法在逻辑上并无漏洞,但算法太费时,代码无法通过测试,所以需要引入更高级的数据结构——trie,简化时间复杂度。
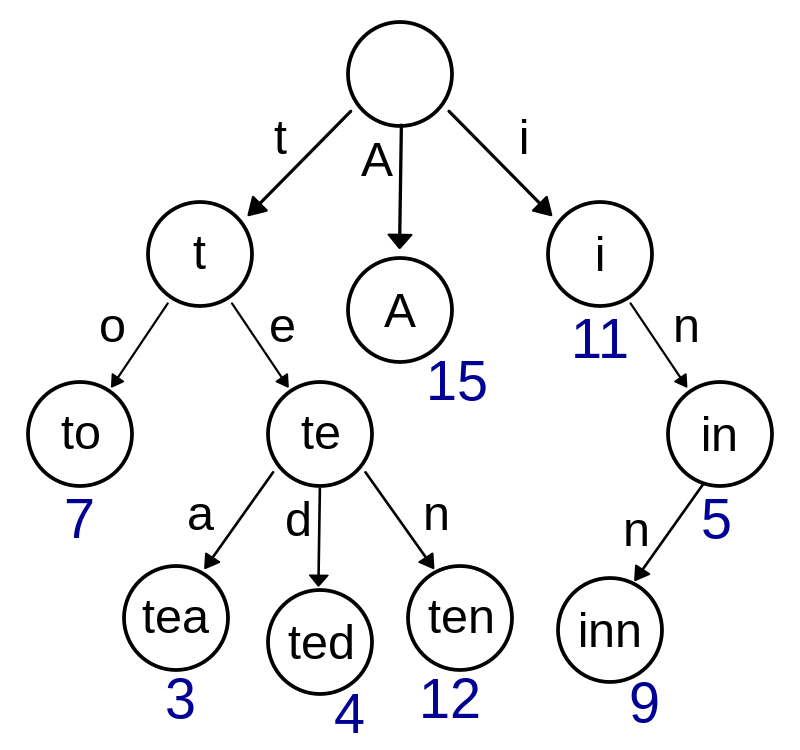
- 简单理解,相对线性数据结构 hashmap,trie 类似一个树状字典。在遍历单词时,如果当前字符存在,就往下继续遍历;如果没有就提前返回 false。每个单词的末尾,即 leaf node,需要标注为 endWord。
- 引入 trie 以后,原本遍历 hashmap 时需要的 O(n)的费时可以简化为 O(1)。
- 为了进一步简化时间复杂度,在 trie 中添加 removeWord 方法:如果单词被找到,就删除它,因为本题中目标单词序列没有重复。。。
# 引入 Trie 后的完整代码如下 🥲
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.children = {}
self.isWord = False
self.refs = 0
def addWord(self, word):
cur = self
cur.refs += 1
for c in word:
if c not in cur.children:
cur.children[c] = TrieNode()
cur = cur.children[c]
cur.refs += 1
cur.isWord = True
def removeWord(self, word):
cur = self
cur.refs -= 1
for c in word:
if c in cur.children:
cur = cur.children[c]
cur.refs -= 1
class Solution:
def findWords(self, board: List[List[str]], words: List[str]) -> List[str]:
root = TrieNode()
for w in words:
root.addWord(w)
ROWS, COLS = len(board), len(board[0])
res, visit = set(), set()
def dfs(r, c, node, word):
if (
r < 0
or c < 0
or r == ROWS
or c == COLS
or board[r][c] not in node.children
or node.children[board[r][c]].refs < 1
or (r, c) in visit
):
return
visit.add((r, c))
node = node.children[board[r][c]]
word += board[r][c]
if node.isWord:
node.isWord = False
res.add(word)
root.removeWord(word)
dfs(r + 1, c, node, word)
dfs(r - 1, c, node, word)
dfs(r, c + 1, node, word)
dfs(r, c - 1, node, word)
visit.remove((r, c))
for r in range(ROWS):
for c in range(COLS):
dfs(r, c, root, "")
return list(res)
Constraints
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12board[i][j]is a lowercase English letter.1 <= words.length <= 3 * 1041 <= words[i].length <= 10words[i]consists of lowercase English letters.- All the strings of
wordsare unique.
对比 79, 升级后的 212 要求算法能够搜索高达 3 * 104 单词序列……考试时,听到这种大数字,基本上预示明眼可见的一些简单解法,肯定是通不过的了……难题登场了……🥲
Big O
- Time:引入 trie 后,复杂度从 O(n * m * 4 * k * 单词长度 )可以简化为 O(n * m * 4 * 单词长度 )
- space:O(k),k 为目标搜寻单词序列长度。如果要搜 1000 个单词,返回 res 长度最坏的时候有 1000 😭
本题十分复杂,如有错误,欢迎大佬评论区指证。
测试
- 序列中一些单词存在,一些单词不存在
- 当然不要忘了重点:一次搜 3000 个单词的极限值……
总结
- 不少难题是由中档、简单档题 循序渐进 + 升级 + 变形 + 组装 而来,例如本题在 79 的 backtracking 等基础之上又组装添加了 trie 元素。欲解难题,需要对基础题有深度理解。
- 一些难题并不是拿到题目后完全没有思路,例如本题……而是那些显而易见的简易思路(例如 brute force)将造成时间复杂度超级复杂,需要引入高档数据结构(如本题涉及的 trie 知识点)又或者高档算法思路(如 dynamic programming🙈)优化……即难题难点所在……😭
- 考试时如果遇上这种题,如果反应不过来先把 brute force + hashmap 的普通解法拿出来给考官讨论下,总比一行代码不写得 0 分强。如果考官暗示 trie,一定要接住……😭